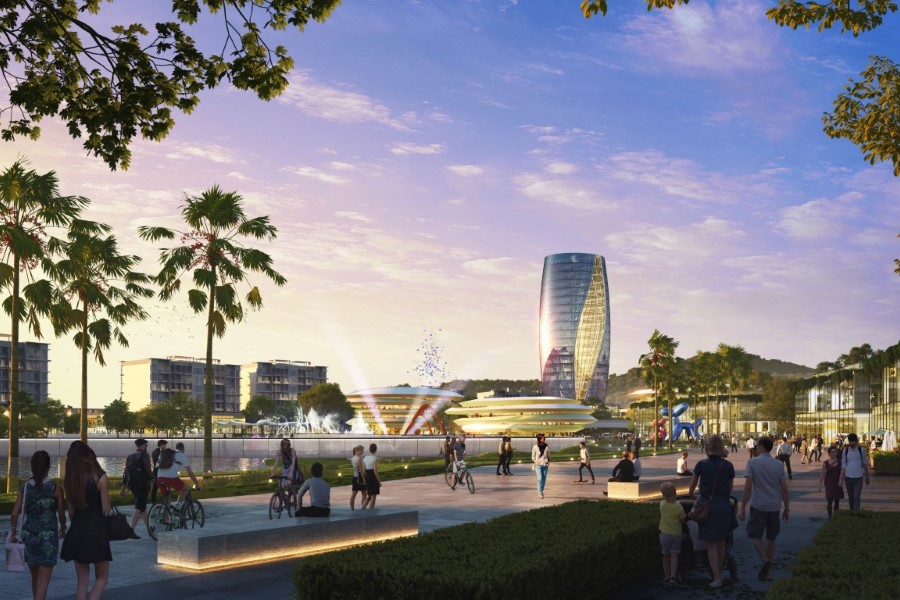
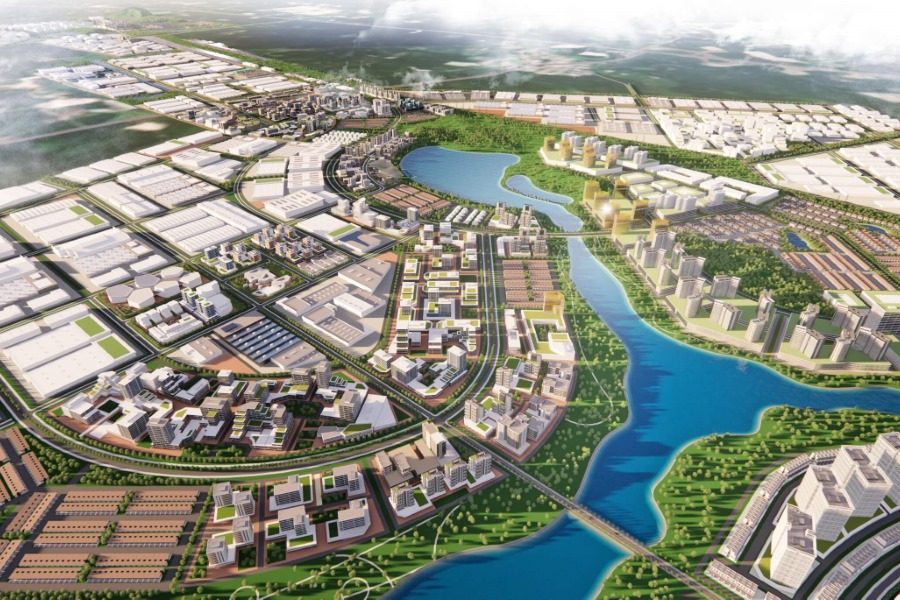
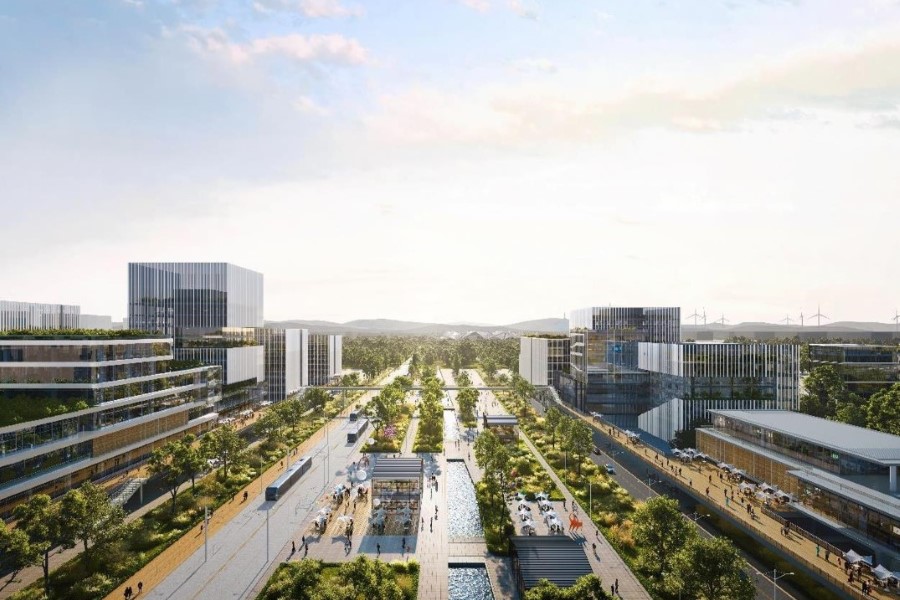
GREEN INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION COMBUSTOR
World’s first net-zero industrial park setting standards for zero-carbon industrial parks
Dr. Zhang QingYu
SJ NORTH ASIA
NOVEMBER 2023
Envision’s battery factory is the key enterprise in Ordos Net-zero Industrial Park, and represents the modern industry plants in the park. This 530m long plant was completed and started its production in April 2022. In April 2023, it has delivered 5 million battery products.
Abstract: Ordos, a resource-based city, is rich in natural resources but also notable for its high carbon emissions. To address this issue, Surbana Jurong Group (SJ Group), an expert in industrial park planning, partnered with green technology pioneer Envision Group to develop a net-zero industrial park in Ordos.
The collaboration aims to organically combine the production and use of green energy through
innovative park design, kickstarting the green industrial revolution. With a comprehensive conceptual
plan benchmarked against leading domestic and international parks, this initiative seeks to facilitate
Ordos’ transition towards a zero-carbon future.
Background of the Net-zero Industrial Park
In the distance among the verdant greenery and industrial grey of factory facades stand rows of
majestic, powerful wind turbines, rotating leisurely in the breeze. The silver-blue photovoltaic panels
gleam under the rays of the sun, as the energy storage and power battery systems are produced in the
factories. This is the world’s pioneering Ordos Net-zero Industrial Park.
Living up to its name, the park attains 80% of its needed energy from wind and photovoltaic sources.
Supplemented by a cooperative protocol with the grid, the park achieves a 100% zero-carbon energy
supply. The park’s digital energy management platform is powered by AIoT, ensuring efficient utilisation.
In September 2020, China put forward the goal of “achieving carbon peak in 2030 and carbon neutrality
in 2060”. In line with this, the Ordos Municipal Government has reached out to distinguished local and
international firms and innovation teams to collaboratively develop the zero carbon Industrial Park
development model, collectively moving forward on the green frontier.
Following China’s “Dual Carbon” target, SJ Group is cooperating with Envision Group to
develop and release the world’s first “International Net-zero Industrial Park Standard”. This standard is
aligned with international standards and is adopted to help enterprises in the park to realise their
net-zero transition.
This standard is aligned with international standards and is adopted to help enterprises in the park to realise their net-zero transition.
To systematically integrate carbon neutrality, a variety of measures — energy conservation, emissions
reduction, carbon sequestration, carbon sinks, and carbon trading — are comprehensively utilised to
achieve a vital balance between the total carbon dioxide or greenhouse gas emissions and carbon
dioxide absorption. This is facilitated by implementing industrial low-carbon transformation, promoting
facility clustering and sharing, and emphasising resource recycling. As a result, a novel zero-carbon
industrial base is established, seamlessly integrating production, ecology, and lifestyle. The “Low
Carbon/Zero Carbon Industrial Park Construction Guide” highlights the low/zero carbon construction
features of the zero-carbon industrial park, mainly reflected in the six systems: energy, transportation
and logistics, construction, infrastructure, production, and ecosystem.
Park Planning - Building a Net-Zero City
Situated in the southern part of Inner Mongolia’s Autonomous Region, Ordos is strategically positioned
to align with various national strategies, including the “Belt and Road Initiative,” the
“China-Mongolia-Russia Economic Corridor,” and the “New Western Land-Sea Corridor.” This grants
Ordos significant potential for accessing European, South-East Asian, and South Asian markets while
increasing interconnectivity with the rest of the global market. By 2020, the central city of Ordos is estimated to accommodate 1.55 million residents and encompass 212 square kilometers of urban construction land. The Ordos Net-zero Industrial Park, with a total area of 73 square kilometers, is located to the west of the central city of Ordos.


New Western Land-Sea Corridor connecting Belt and Road (left) and Inner Mongolia ‘One Core and Double Stars’ City-Town Layout (right)

The Belt and Road Initiative
After considering conditions such as geographical factors and relevant plans, the SJ Group
proposes that the planning and construction of the Net-zero Industrial Park should be geared towards
strengthening connections with the global and regional markets with a priority of optimising external
transportation and the integration of outer transportation channels.
Furthermore, the masterplan accounts for the relationship between the park and the central city, adopting
a people-oriented approach in achieving industry-city integration. The SJ Group also
respects the natural and cultural characteristics of Ordos and the park itself. The masterplan incorporates
the natural landscape into the park, creating a unique appearance for the future industrial park.
The masterplan incorporates the natural landscape into the park. It creates a unique industrial park of the future.
Drawing lessons from the Suzhou Industrial Park, the first Sino-Singapore governmental cooperation
project that SJ delivered in 1994, Ordos Net-zero Industrial Park
focuses on three spatial planning features.
Firstly, it creates a clear axis, based on the way the functional layout and spatial creation are
established. Then, it considers production and living functions in a human-oriented approach,
establishing a new industrial city that is liveable and work-friendly by constructing a service facility
system combining core and nodes. Finally, it organises traffic and passenger and cargo diversion
through transport route optimisation, providing cost-efficient and effective transportation.
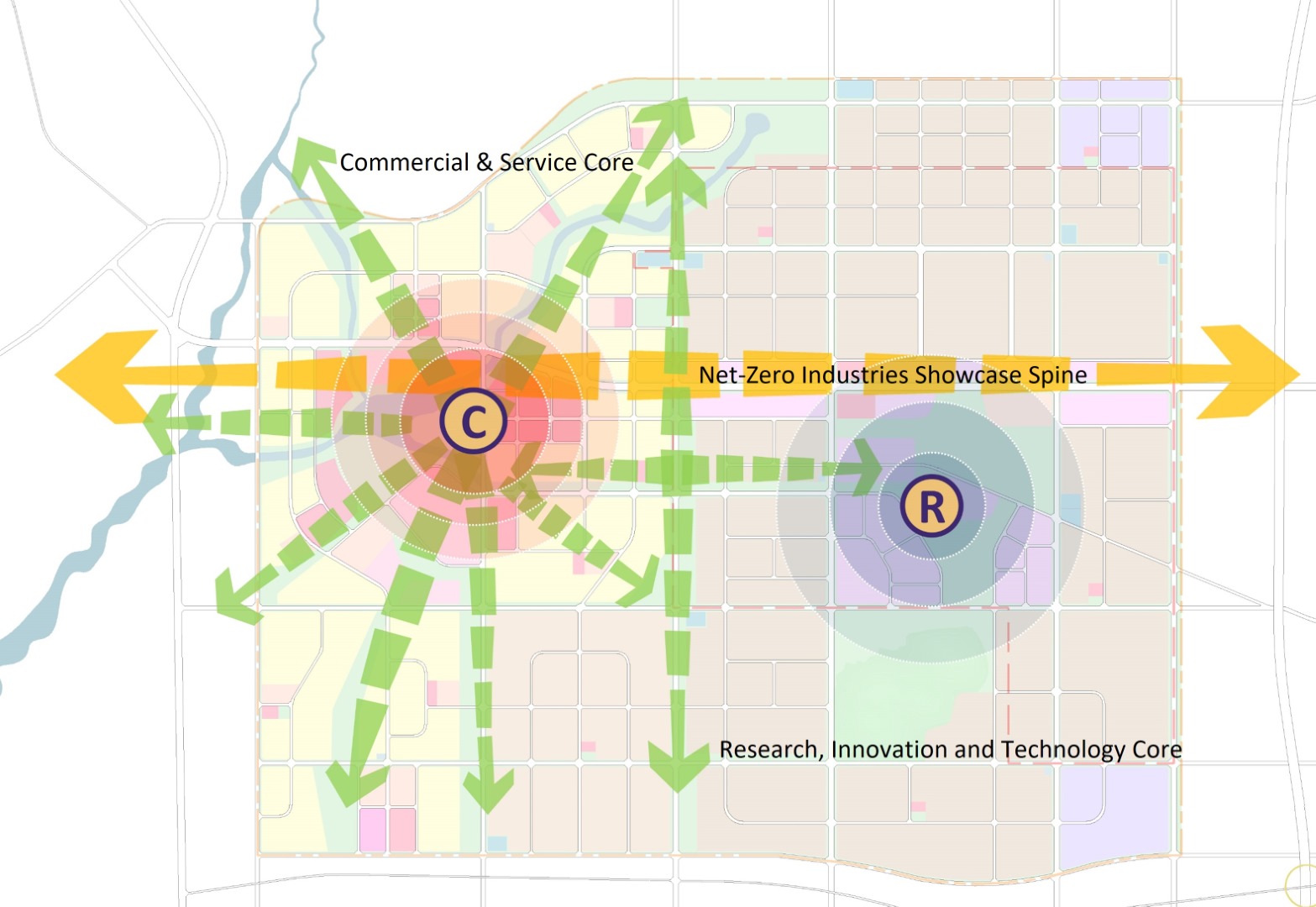
Creation of a clear axis for organisation of functions and space styles along the axis
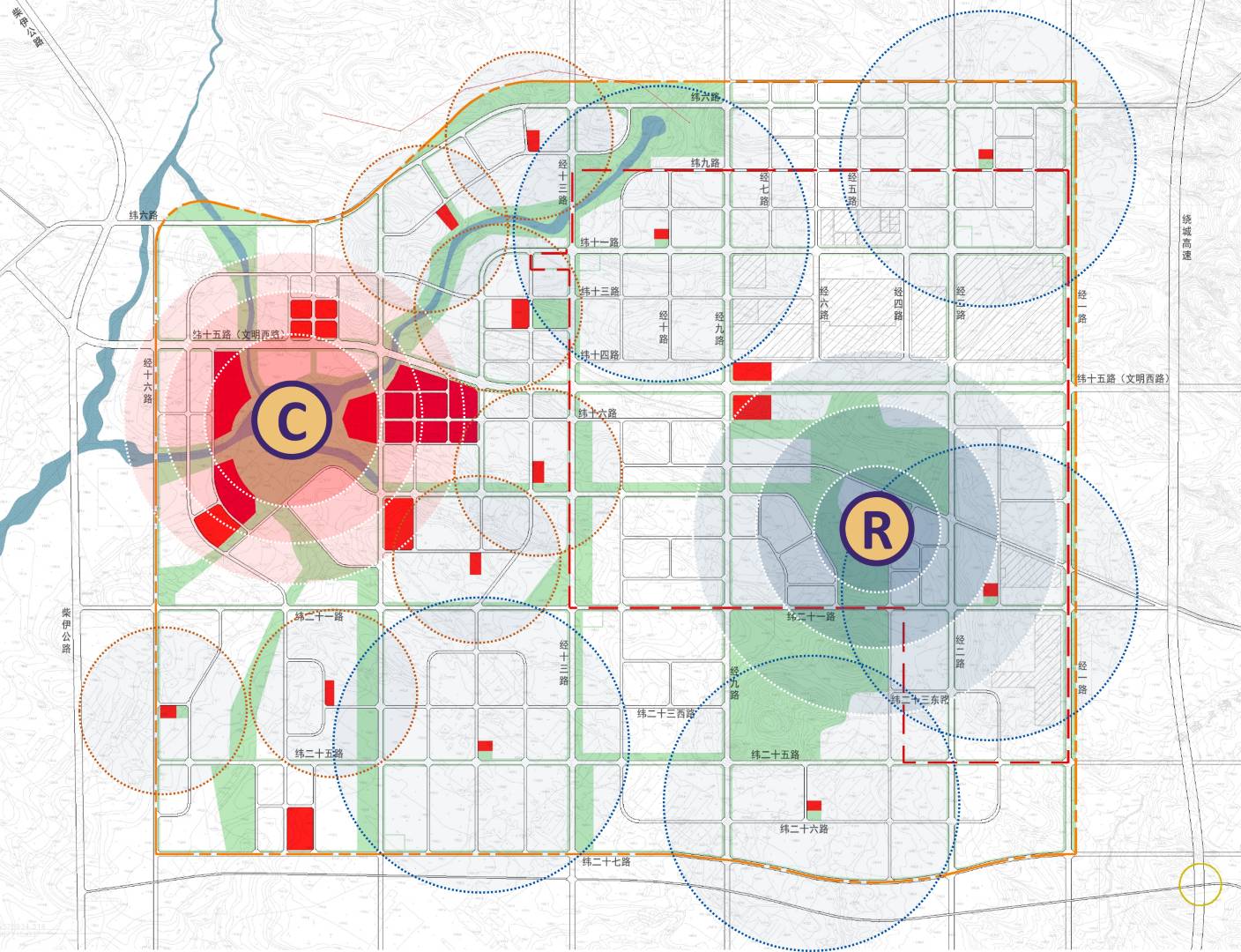
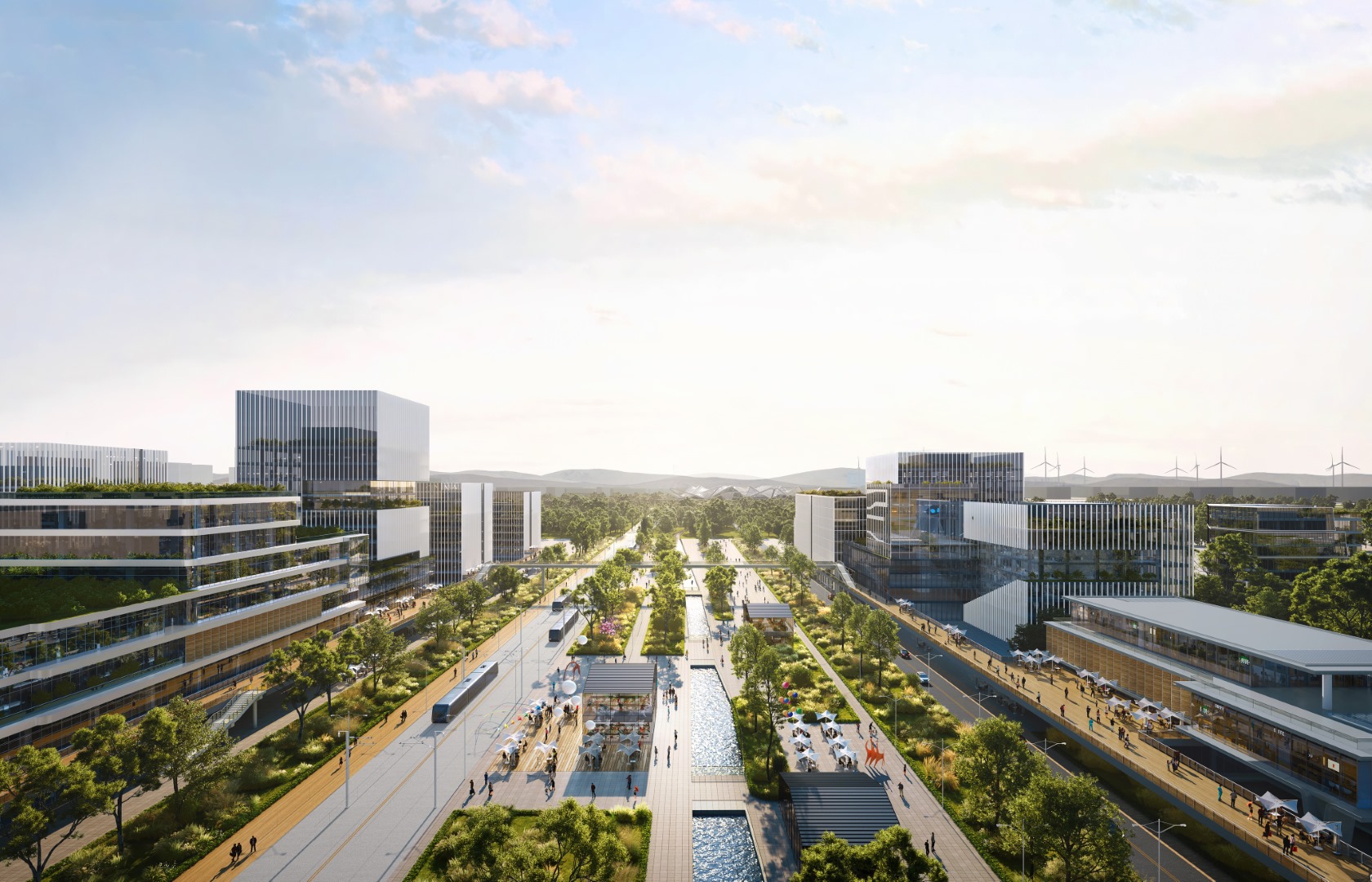
Commercial & Service System
Careful urban planning and policy-making are
crucial to avoid the ghost city phenomenon.
Thus, it is important to assess market
demand and ensure that development aligns
with the needs and preferences of the
population. This includes considering factors
such as population growth, employment
opportunities, and transportation
infrastructure. Furthermore, adopting
sustainable development practices can help
optimise land and space utilisation.
Emphasising mixed-use developments, where
residential, commercial, and recreational
facilities coexist, can create vibrant and
dynamic urban environments. This allows for
reduced commuting distances and fosters a
sense of community.
Logistics Transportation
Being the world’s first zero-carbon industrial park, Ordos Net-zero Industrial Park is considered a pilot
project locally and beyond that, a benchmark for the wider world. The Ordos Net-zero Industrial Park is
positioned as a global showcase of “ecological priority and green development”. It serves as a new
engine propelling Ordos’ economic development, as well as a modern cutting-edge green city for living,
working and visiting. Around the zero-carbon construction goal, the planning strategy is featured in five
aspects: green energy, spatial layout, green transportation, modern production and living, and
establishing a green carbon sink.
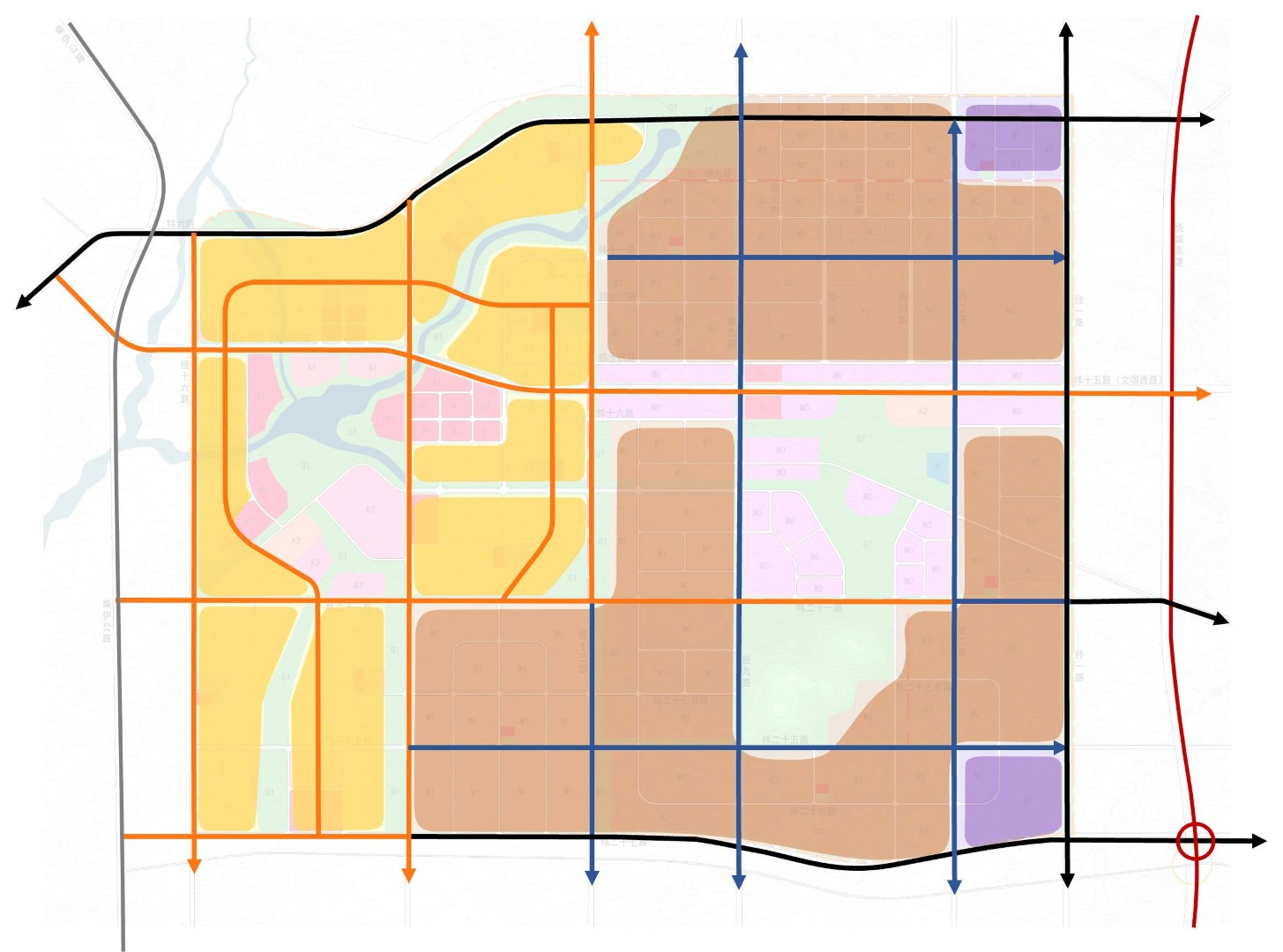
Logistics Transportation

Green Energy lies in abundant wind and lights, and existing power resources of Inner Mongolia. An
energy island is planned as the cloud management and deployment core of regional green energy. As
envisioned, this island serves as a control centre, storing and distributing green energy with fully
visualised operations. Simultaneously, the park serves as a hotbed to explore and put into practice low
or zero carbon technology such as sewage source heating, solar heating, new energy boilers, air
source heat pumps, etc.
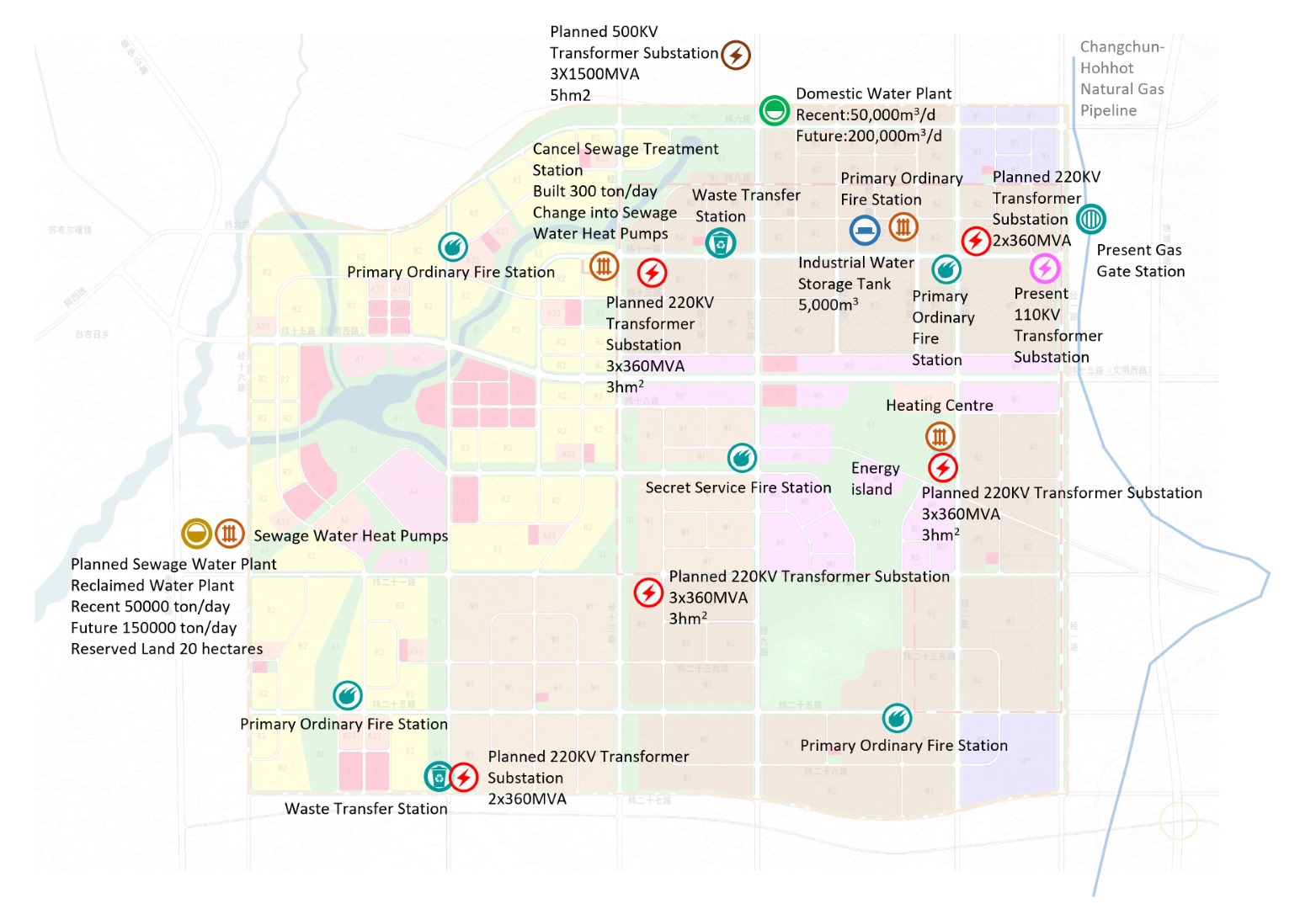
Energy Island Facility Distribution Map
Spatial layout focuses on creating industrial clustering concentrating on space, facilitating the
interaction of upstream and downstream industrial chains.
It is proposed to set up different graded and
classified service facilities in each functional area to
meet the needs of workers and residents. Efforts are
made to guarantee the convenience and accessibility
of public service facilities when reducing the traffic
volume of daily activities.
Accounting for commuting distance and
time, the production and living facilities are arranged in a manner that optimises the utilisation of land,
space and various facilities, thereby reducing pendulum traffic and avoiding the “Ghost City”
phenomenon.
Green Transportation is essential to reduce carbon emissions associated with transportation. The
zero-carbon Industrial Park can improve factory layout, logistics routes, and turnover efficiency by
integrating and optimising its transportation and logistics infrastructure. By implementing a public
transport system, carbon emissions are effectively reduced. Promoting the use of vehicles that run on
alternative fuel such as hydrogen gas and building infrastructure to support this transition further
reduces carbon emissions.
Modern production and living philosophy encourage a green lifestyle and production process. Energy
conservation should be centred, and measures include: policies promoting the use of energy-efficient
appliances, greener methods of travel, and administrative planning that reduce household waste. On a
larger scale, this involves enforcing an energy-saving barrier to entry for manufacturing firms,
improving recycling efficiency and resource management through infrastructural development and
policy, or policy requiring newer building to comply to national energy-efficiency standards — to adopt
distributed energy supply equipment, and to apply intelligent statistical system monitoring various types
of resource consumption and carbon emissions.
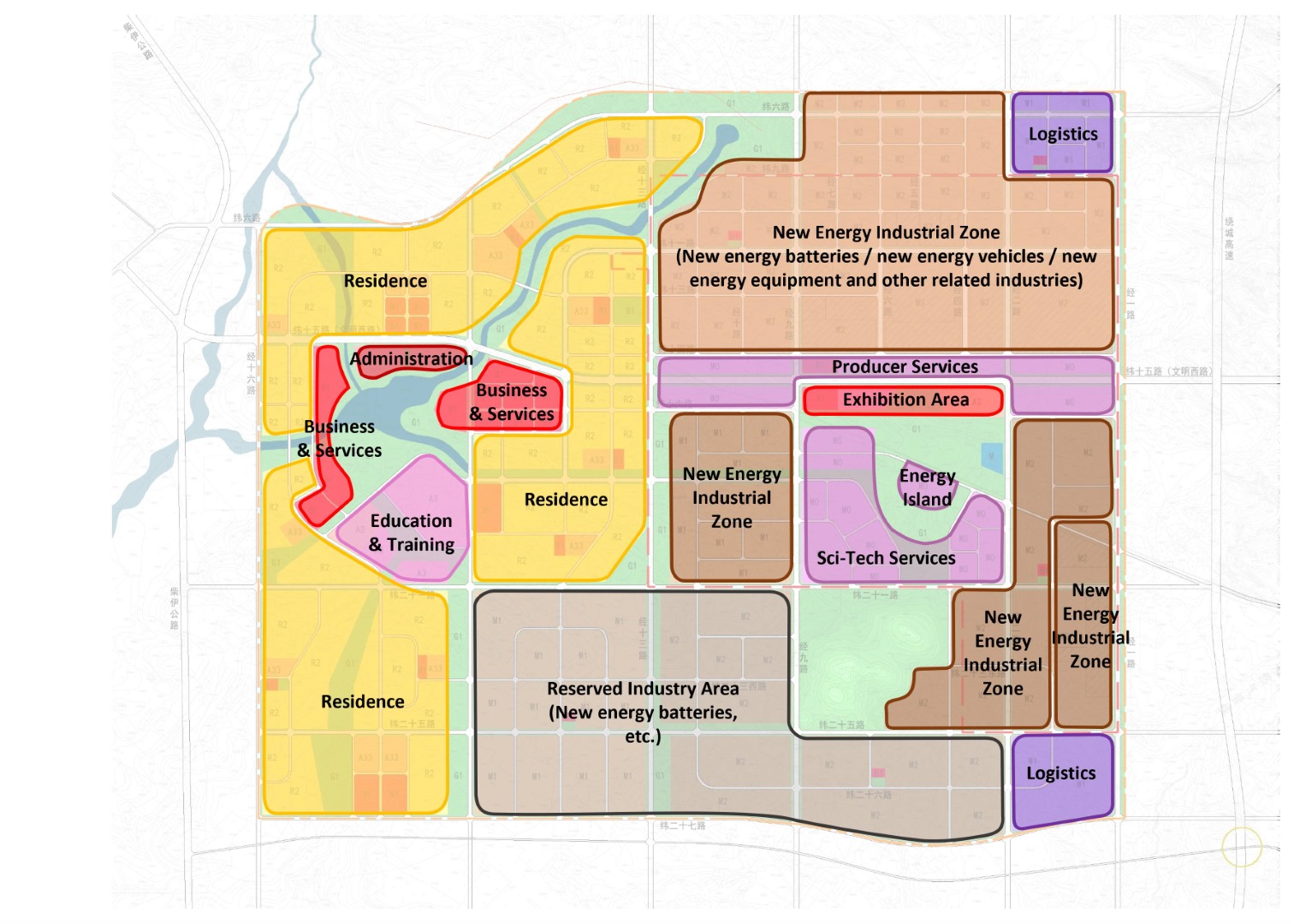
Functional Zones

The “Green Carbon Sink” method can be implemented to aid efforts. It involves the formation of a
green space in the park via building an artificial lake, energy island display garden, and road protection
facilities. Green landscape belts connect the various elements, allowing them to form the green space.
This system simultaneously enhances production while elevating the lived environment, utilising
carbon-sequestering to lower carbon emissions. The green-coverage ratio and ecosystem balance are
bolstered by populating the space with drought and pest resistant flora. This measure also encourages
efficient utilisation of space while allowing for innovative practices such as vertical greening, roof
greening, and 3-D greening.
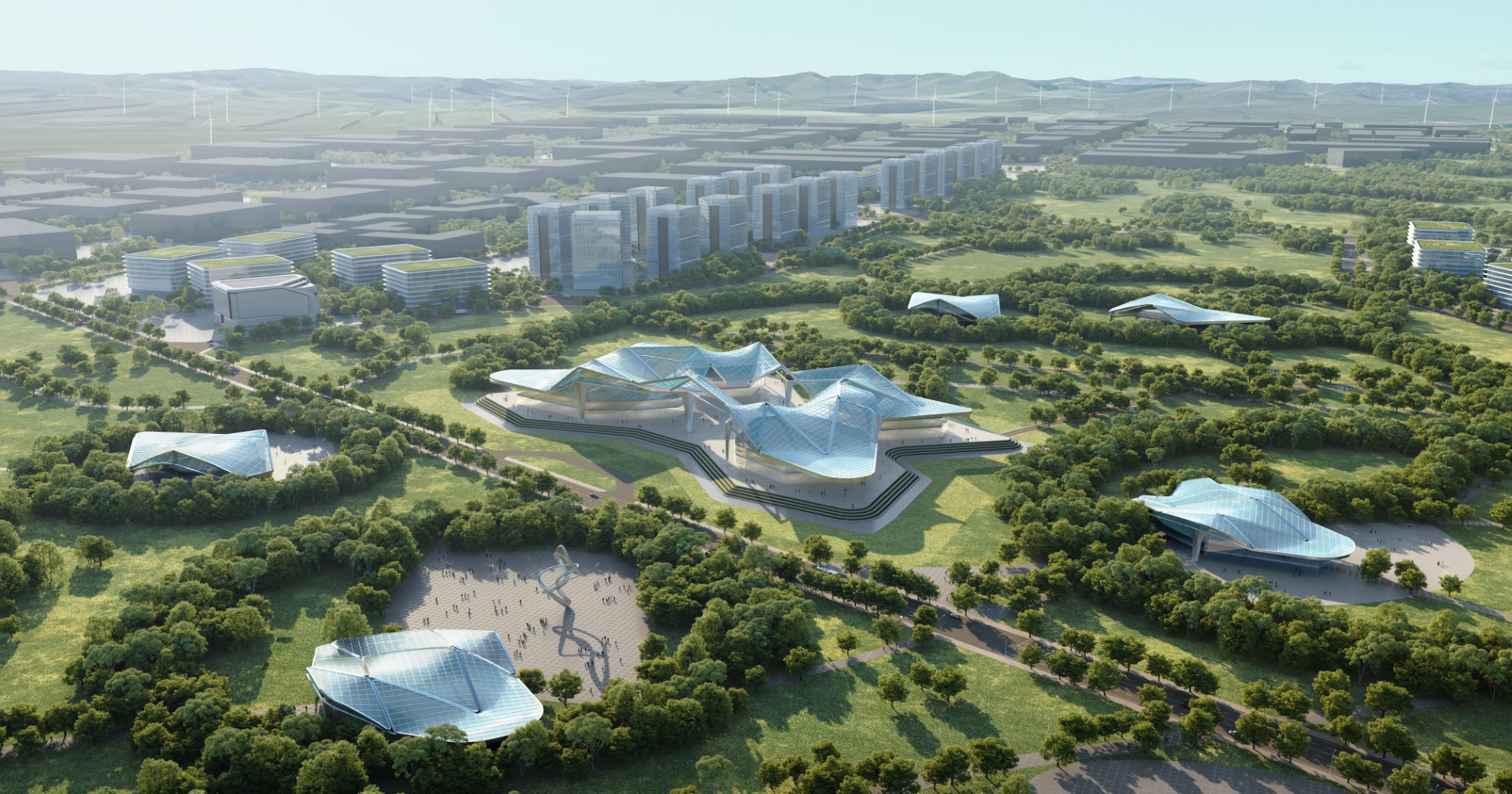


Multiple green spaces
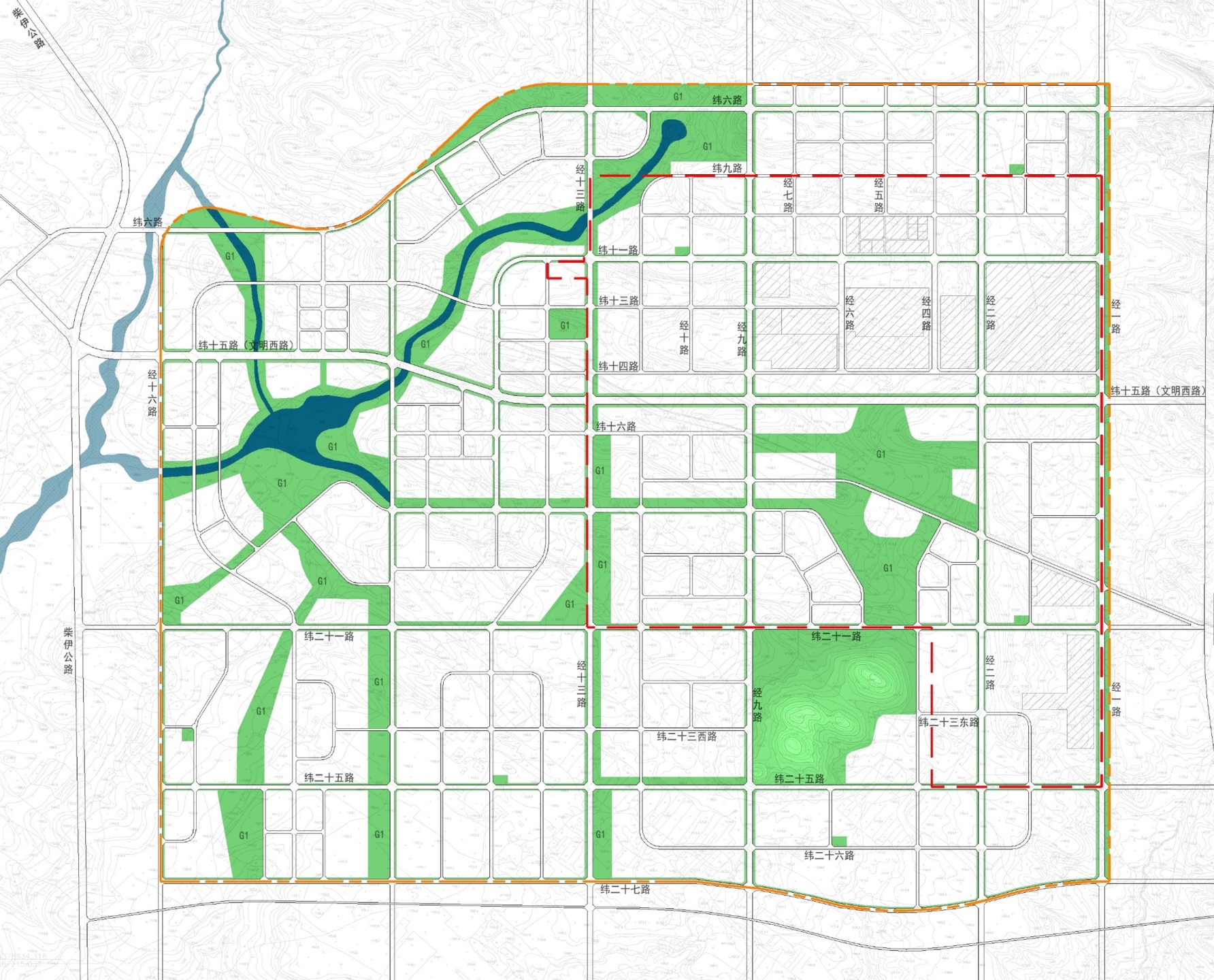
Green Space and River System
Boosting the Green Industrial Revolution
The vision of the masterplan is to attract leading enterprises to drive development of the industrial chain
and position relevant industries on the periphery of the park. SJ Group has developed an
industrial positioning plan and urban design concept to provide a successful blueprint for the development,
making Ordos a new engine, one that is driving the green revolution. The net-zero industrial park is a key
piece in the ground-breaking green economic revolution. To achieve the “Dual Carbon” objective, the plan
combines production and use of green energy, resulting in a giant leap towards low or even zero carbon
consumption and emission. Pilot projects are already underway in the resource-rich regions of northern
China, paving the way for the future.
The completion of the net-zero industrial park by 2025 will result in a cumulative reduction of 100 million tons of carbon dioxide emissions.
The completion of the net-zero industrial park by 2025 will result in a cumulative reduction of 100 million
tons of carbon dioxide emissions. It will consume 15 billion kilowatt-hours of green electricity annually
and generate an output value exceeding RMB 100 billion. Along with that, it will create 100,000 jobs in
the science and tech industry. The Ordos Net-zero Industrial Park will serve as a global demonstration
of net-zero industrial, intelligent and intentional innovation, and a futuristic ecological city, pioneering a
trend of green and low-carbon development worldwide.
The SEEDS Journal, started by the architectural teams across the Surbana Jurong Group in Feb 2021, is a
platform for sharing their perspectives on all things architectural. SEEDS epitomises the desire of the Surbana
Jurong Group to Enrich, Engage, Discover and Share ideas among the Group’s architects in 40 countries, covering
North Asia, ASEAN, Middle East, Australia and New Zealand, the Pacific region, the United States and Canada.
Articles at a glance